Distribution: marine; all oceans. Upper lobe of caudal fin greatly elongate, caudal fin almost one-half of total length; third to fifth gill openings over origin of pectoral fin. Ovoviviparous, embryos feeding on yolk sac and other ova produced by the mother (Ref. 50449).
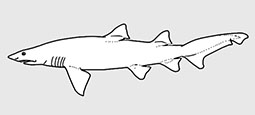
Carchariidae - (Ragged-tooth sharks)
Distribution: Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans, cool temperate to tropical. Gill openings all in front of pectoral fin, relatively large but not extending onto dorsal surface of head; eyes relatively small; caudal peduncle without a lateral keel; caudal fin asymmetrical with relatively short ventral lobe. Ovoviviparous, embryos feeding on yolk sac and other ova produced by the mother (Ref. 50449), except Carcharias taurus. Maximum length 3.6 m.

Cetorhinidae - (Basking sharks)
Marine, all oceans, highly migratory. Gill openings exceptionally large; gill rakers elongate, plankton feeders, teeth reduced. The tail is nearly symmetrical with keel on caudal peduncle. Fifth gill opening in front of pectoral fin. The family contains the world's second largest fish, reportedly reaching 1,520 cm TL (Ref. 247). Ovoviviparous, embryos feeding on yolk sac and other ova produced by the mother (Ref. 50449).

Lamnidae - (Mackerel sharks or white shark)
Distribution: Global. Primarily in the upper part of the water column over the continental shelves and open ocean (Ref. 119696). Morphology: Large sharks with pointed snouts and spindle-shaped bodies. Large gill openings. First dorsal fin large, high, erect and angular or somewhat rounded. Second dorsal and anal fins minute. Caudal peduncle with a distinct keel; large teeth; fifth gill opening in front of pectoral fin; spiracle sometimes absent. Food: Fast swimming predators; some are maneaters. Reproduction: Ovoviviparous, embryos feeding on yolk sac and other ova produced by the mother (Ref. 50449). Litters of 1-17 or more live pups (In the uterus, developing lamnid shark embryos are nourished by a yolk-sac initially, but once that is exhausted they consume fertilized and unfertilized eggs entering from the oviduct (Ref. 119696). Maximum length up to 6.4 m or more. Maximum age: at least 27 years (Ref. 119696).
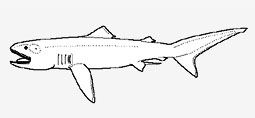
Megachasmidae - (Megamouth sharks)
Known only from the type locality near the Hawaiian Islands in 165 m depth. Trunk cylindrical and somewhat compressed, stout. Head very long, snout extremely short but broadly rounded, huge terminal mouth that extends behind the eyes. Gigantic filter-feeding shark. Ovoviviparous, embryos feeding on yolk sac and other ova produced by the mother (Ref. 50449).

Mitsukurinidae - (Goblin shark)
Distribution: scattered in eastern and western (French Guiana) Atlantic, South Africa, and western Pacific. Snout with a greatly elongated and flattened projection; jaws very protrusible; precaudal pit absent; eyes small; ventral lobe of caudal fin not developed. Ovoviviparous, embryos feeding on yolk sac and other ova produced by the mother (Ref. 50449). Maximum length 3.3 m.
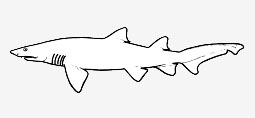
Odontaspididae - (Sand tiger sharks)
Distribution: Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans, cool temperate to tropical. Gill openings all in front of pectoral fin, relatively large but not extending onto dorsal surface of head; eyes relatively small; caudal peduncle without a lateral keel; caudal fin asymmetrical with relatively short ventral lobe. Ovoviviparous, embryos feeding on yolk sac and other ova produced by the mother (Ref. 50449), except Carcharias taurus. Maximum length 3.6 m.
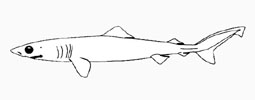
Pseudocarchariidae - (Crocodile sharks)
Distribution: scattered localities, coastal to oceanic, subtropical to tropical, Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Eyes exceptionally large, without a nictitating membrane; five gill openings extending onto dorsal surface of head; two low, angular dorsal fins; caudal peduncle with upper and lower precaudal pits and with low lateral keel. Ovoviviparous, embryos feeding on yolk sac and other ova produced by the mother (Ref. 50449). Maximum length 1.1 m.
Note: Families with unknown counts of dorsal or anal spines are also included
