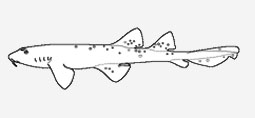
Brachaeluridae - (Blind sharks)
Distribution: western South Pacific (Australia). Common, small (< 1.3 m), inshore bottom sharks confined to temperate and tropical continental waters of Australia, ranging in depth from the intertidal down to 110 m. Known food items include small fishes, crustaceans, cuttlefish and sea anemones. Nasoral grooves, perinasal grooves, long barbels, small transvers mouths in front of eyes, large spiracles below eyes. Two spineless dorsal fins and an anal fin, the second dorsal origin well ahead of the anal origin, and a short precaudal tail much shorter than the head and body. Ovoviviparous, embryos feed solely on yolk (Ref. 50449). Maximum length 1.2 m.
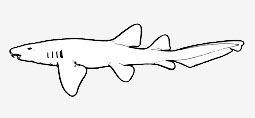
Ginglymostomatidae - (Nurse sharks)
Marine, all oceans. Small to large sharks with nasoral grooves, short to long barbels, small spiracles behind eyes. Two spineless fins and an anal fin, the second dorsal origin well ahead of the anal origin. A short precaudal tail, much shorter than the head and the body. These are common, small to large, nocturnal, inshore bottom sharks with a circumglobal distribution in subtropical and tropical waters, in depths from the intertidal down to at least 70 m. These sharks cruise and clamber on the bottom with their mouths and barbels close to the substrate while searching for food. They use their short, small mouths and large mouth cavities as a bellows to suck in their prey. Food items: bony fish, crabs, shrimps, lobsters, squids, octopuses, corals, sea urchins, sea squirts. Young born fully developed.

Hemiscylliidae - (Bamboo sharks)
Tropical western Pacific from Madagascar in the west to Japan, the Philippines and the Australian region in the East. Two dorsal fins without spines. Anal fin present. Five gill slits. Mouth ventral. Fourth and fifth gill opening behind origin of pectoral fin. Small, slender sharks (max 1 m) with nasal grooves, short barbels, large spiracles below eyes. Nearly cylindrical in cross-section. Precaudal tail longer than head and body length. Inshore bottom sharks of continental waters. Young hatch from round egg cases. Food probably includes small bottom fishes and invertebrates. Relatively sluggish and harmless, spending most of their time resting on the bottom. Used as foodfishes (Ref. 9710).
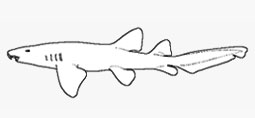
Orectolobidae - (Carpet or nurse sharks)
Distribution: Indo-Pacific. Body depressed, head very broad and flattened. Mouth inferior. Gill openings 5, the fourth and fifth behind origin of pectoral fin, over the base. Nostril with a well developed barbel. A deep groove leads from nostril to mouth. Head with lateral flaps of skin. First dorsal fin posteriorly located. Bottom sharks of warm-temperate to tropical continental waters of the western Pacific, occuring from intertidal down to at least 110 m. Ovoviviparous, with large litters of 20 or more young.

Parascylliidae - (Collared carpet sharks)
Temperate and tropical, continental waters of the western Pacific. Small (< 1 m), slender sharks with cat-like eyes with subocular pockets. first dorsal origin behind pelvic bases. Narrow nasoral grooves, medial barbels. Food is little known, but probably includes small fishes, crustaceans, and other bottom invertebrates. Caudal fin with its upper lobe not elevated above the body axis, with a strong terminal lobe and subterminal notch but no ventral lobe (Ref. 13572).
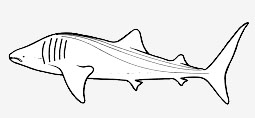
Rhincodontidae - (Whale shark)
Distribution: tropical waters. Often near the surface, sometimes in schools of up to hundreds of sharks. Whale sharks are apparently highly migratory, probably timed with blooms of planktonic organisms. Five exceptionally large gill openings, the fifth behind origin of pectoral fin, over fin base. Elongated gill rakers. Mouth terminal. Reduced teeth. A unique color pattern of light spots and vertical and horizontal stripes, in the form of a checkerboard. Planktivorous. Maximum reported length 13.7 m, (world's largest fish). Young probably born fully developed.

Stegostomatidae - (Zebra sharks)
Tropical inshore sharks of the Indo-West Pacific, very common on coral reefs. Large sharks that combine a broad, low caudal fin about as long as the rest of the shark. Nasal grooves, barbels, a small transverse mouth in front of the lateral eyes. Two spineless dorsal fins, the first dorsal much larger than the second. Prominent ridges on the sides of the body. A banded (in juveniles) or spotted color pattern. Oviparous, laying eggs in large, dark brown or purplish-black cases with fine lateral tufts of hairlike fibers. Feeds primarily on molluscs (gastropods and bivalves) but also crabs and shrimps and small bony fishes. Young hatch from egg cases at a size of 20 to 26 cm.
Note: Families with unknown counts of dorsal or anal spines are also included