Myxines (hagfishes) >
Myxiniformes (Hagfishes) >
Myxinidae (Hagfishes) > Myxininae
Etymology: Myxine: Ancient Greek word for a slimy fish: myxa, slime; -inus, one who, referring to copious amounts of slime produced by M. glutinosa. (See ETYFish); glutinosa: Latin for viscous or sticky, referring to its seeming ability to turn water into slime. (See ETYFish).
More on author: Linnaeus.
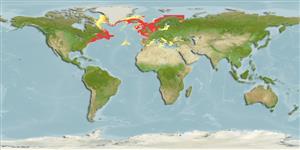
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Écologie
marin bathydémersal; non migrateur; profondeur 20 - 1200 m (Ref. 117245), usually 27 - 460 m (Ref. 119696). Boreal; 2°C - 13°C (Ref. 119696); 72°N - 24°N, 89°W - 41°E
North Atlantic: Murmansk to the Mediterranean Sea; Greenland to USA. Absent in eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea. Only hagfish in the Northeast Atlantic.
Length at first maturity / Taille / Poids / Âge
Maturity: Lm ?, range 25 - ? cm
Max length : 95.0 cm TL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 119696); common length : 30.0 cm TL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 35388); common length :40 cm TL (female)
Jawless mouth, single nasal aperture, only a single pair of external gill openings, no operculum or covering fold of skin. Grayish or reddish brown above, either plain. Variations in color correspond to the color of the sea bottom.
Benthic with reported depths to 782 off Greenland; 960 m in Northwestern Atlantic; and 1,100 m off Norway (Ref. 119696). Found on muddy bottoms where they hide in the mud. Slime is used for defense. Feeds chiefly on dead and dying fish of varying species by boring into the body and consuming viscera and musculature. Chiefly nocturnal. Its eggs are few in number about 19-30 and large (20-25 mm), the horny shell has a cluster of anchor-tipped filaments at each end.
Copulatory organ absent. The gonads of hagfishes are situated in the peritoneal cavity. The ovary is found in the anterior portion of the gonad, and the testis is found in the posterior part. The animal becomes female if the cranial part of the gonad develops or male if the caudal part undergoes differentiation. If none develops, then the animal becomes sterile. If both anterior and posterior parts develop, then the animal becomes a functional hermaphrodite. However, hermaphroditism being characterised as functional needs to be validated by more reproduction studies (Ref. 51361 ). Probably breed throughout the year in deep water (Ref. 35388).
Fernholm, B., 1998. Hagfish systematics. p. 33-44. In J.M. Jørgensen, J.P. Lomholt, R.E. Weber and H. Malte (eds.) The biology of hagfishes. Chapman & Hall, London. 578 p. (Ref. 31276)
Statut dans la liste rouge de l'IUCN (Ref. 130435)
Menace pour l'homme
Harmless
Utilisations par l'homme
Pêcheries: sans intérêt
Outils
Articles particuliers
Télécharger en XML
Sources Internet
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 1 - 10.2, mean 5.3 °C (based on 550 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00115 (0.00045 - 0.00296), b=3.03 (2.80 - 3.26), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this (Sub)family-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Niveau trophique (Ref.
69278): 4.5 ±0.0 se; based on diet studies.
Résilience (Ref.
120179): Faible, temps minimum de doublement de population : 4,5 à 14 années (Fec= 20-30).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): High vulnerability (58 of 100).
Climate Vulnerability (Ref.
125649): Moderate vulnerability (38 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 7.79 [2.08, 25.45] mg/100g; Iron = 0.278 [0.095, 0.782] mg/100g; Protein = 2.26 [0.00, 6.14] %; Omega3 = 0.301 [0.116, 0.790] g/100g; Selenium = 18.8 [5.5, 64.6] μg/100g; VitaminA = 11 [2, 52] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.281 [0.133, 0.569] mg/100g (wet weight);